Breaking into the tech industry as a Quality Assurance (QA) Tester is one of the best ways for fresh graduates and career changers to begin. QA is more than just “finding bugs”, it’s about ensuring that software products meet quality standards and deliver a smooth user experience. If you’re passionate about details, curious about how things work, and enjoy problem-solving, QA can be an excellent starting point.
In this guide, we’ll walk through what QA testing is, why it matters, and how you can start your journey step by step.
Why QA Testing Matters
Every piece of software, whether it’s a mobile app, a website, or an enterprise system, must go through rigorous testing before release. A single overlooked bug can cause financial loss, security breaches, or a poor user experience. That’s why QA testers are critical: they are the guardians of product quality.
As a QA tester, you’ll bridge the gap between developers and end-users, ensuring that software functions properly, is reliable, and matches business requirements.
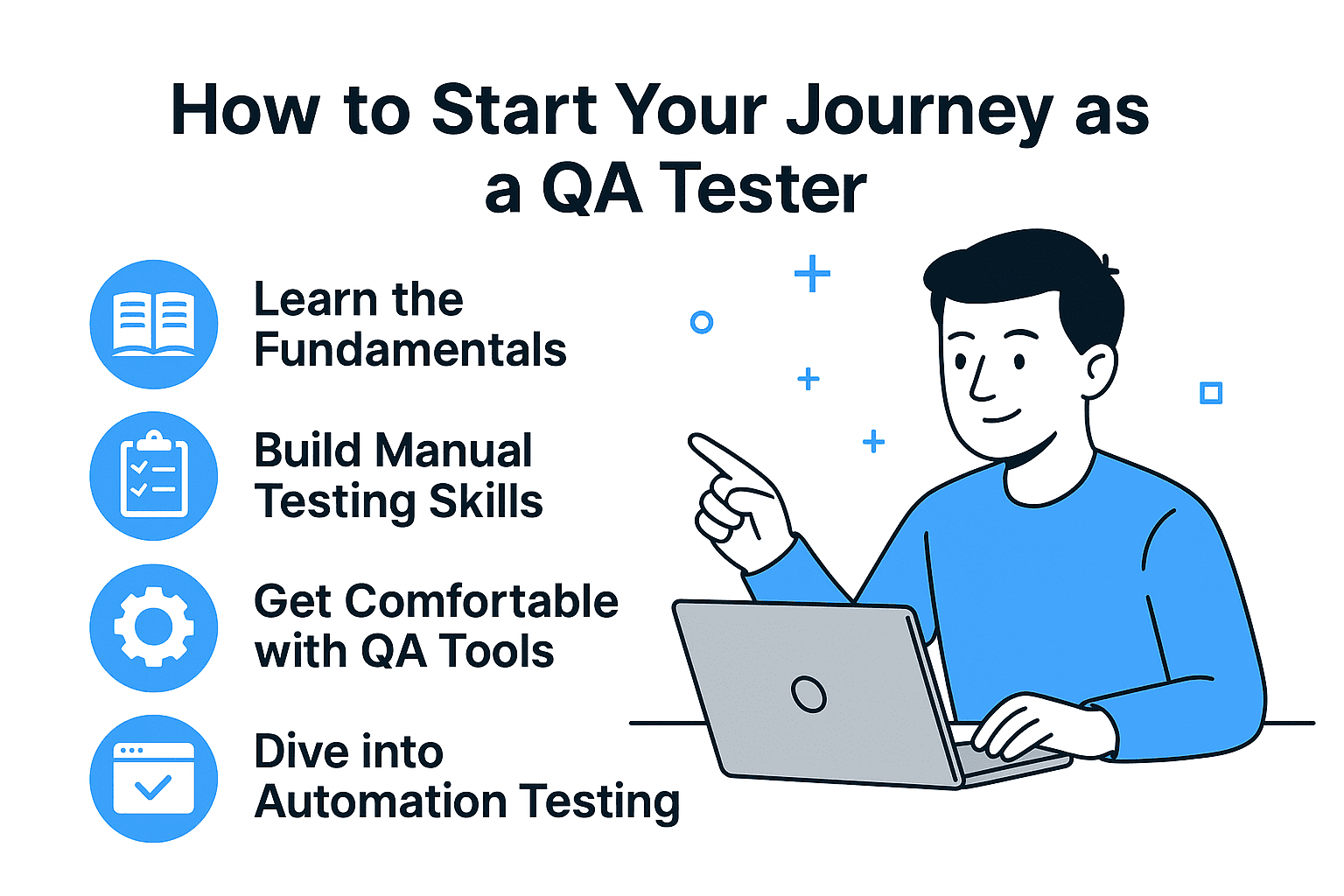
Step 1: Learn the Fundamentals of Software Testing
Before diving into tools or automation, you need a solid foundation:
- Understand the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) – how software is built from planning to deployment.
- Study the Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC) – the steps of planning, designing, executing, and closing tests.
- Know the Testing Types – unit, integration, system, regression, user acceptance testing (UAT).
- Black-box vs. White-box testing – two different approaches: testing without knowing internal code vs. with code insights.
👉 Recommended reading: “Foundations of Software Testing” by Rex Black.
Step 2: Build Manual Testing Skills
Before automation, every tester must master manual testing. This teaches you how to think like a tester and spot issues:
- Learn how to write test cases and test plans.
- Practice exploratory testing, trying out software without strict scripts to uncover hidden issues.
- Document bugs clearly with steps to reproduce, screenshots, and expected vs. actual behavior.
👉 Tools to start: Excel/Google Sheets for test cases, and JIRA or Bugzilla for bug tracking.
Step 3: Get Comfortable with QA Tools
Companies expect you to use industry-standard tools. Start with:
- Bug & Task Tracking: JIRA, Trello, Bugzilla
- Test Management: TestRail, Zephyr
- Collaboration: Confluence, Slack, GitHub (basic version control is useful)
Step 4: Learn a Programming Language
While manual testing doesn’t always require coding, learning at least one language is essential for automation. The most common choices are:
- Python – beginner-friendly and widely used in automation frameworks.
- Java – popular in enterprise testing with Selenium.
Focus on basics: loops, conditions, functions, and object-oriented programming (OOP).
Step 5: Dive into Automation Testing
Automation testing is where you can truly grow as a QA professional. Start with:
- Web Testing: Selenium WebDriver, Cypress, Playwright
- API Testing: Postman, REST Assured
- Mobile Testing: Appium (optional, if you want to test mobile apps)
Automation saves time, increases accuracy, and makes you more valuable in the job market.
Step 6: Understand Agile and DevOps
Most companies today use Agile methodologies like Scrum. As a QA, you’ll join sprints, daily stand-ups, and retrospectives. You’ll also hear about CI/CD (Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery), where testing is integrated into automated pipelines.
Learning the basics of Agile and CI/CD tools like Jenkins or GitHub Actions will set you apart from other beginners.
Step 7: Develop Soft Skills
A successful QA tester isn’t just technical, they’re also strong communicators and critical thinkers. You should:
- Write clear, concise bug reports.
- Ask the right questions and challenge assumptions.
- Collaborate effectively with developers, designers, and product managers.
Remember: QA is as much about people as it is about technology.
Step 8: Build a Portfolio
Just like developers, QA testers can showcase their work:
- Document sample test cases and bug reports.
- Contribute to open-source projects by testing them.
- Create small automation projects and share them on GitHub.
This gives you real-world practice and something to show employers.
Step 9: Apply for Jobs and Internships
When applying for your first QA role, focus on:
- Internships or entry-level QA tester positions.
- Highlighting attention to detail and problem-solving skills.
- Demonstrating knowledge of tools and testing basics, even if you lack work experience.
Tip: Many startups are willing to hire fresh graduates who show initiative and willingness to learn.
Conclusion
Starting your journey as a QA tester doesn’t require years of experience, it requires curiosity, persistence, and continuous learning. Begin with manual testing, master the fundamentals, then gradually move into automation and advanced tools. Along the way, build your portfolio, sharpen your communication, and stay updated with industry trends.
Remember: QA is not just about “breaking things”, it’s about ensuring quality and making technology more reliable for everyone.
🤝 Need a Custom RSVP System or Dashboard?
I help businesses build tools that actually work — even on tight deadlines.
Whether you're planning an event, need internal tools, or want a custom dashboard for your team — I can help.
Reach out
📧 Email: safi.abdulkader@gmail.com | 💻 LinkedIn: @abdulkader-safi | 📱 Instagram: @abdulkader.safi | 🏢 DSRPT
Drop me a line, I’m always happy to collaborate! 🚀